FIRE MONITORING AND BURNED AREA MAPPING
Wildfire is a natural hazard and can be described as any uncontrolled and non-prescribed combustion or burning of plants in a natural setting such as a forest, grassland, brush land or tundra, which consumes the natural fuels and spreads based on environmental conditions (e.g., wind, topography). Wildfire can be caused by human actions, extreme drought or, more rarely, by lightning.

Fire monitoring is one of the main applications of satellite information and aims to detect a forest fire as soon as it starts and then to track its spatial and temporal evolution.
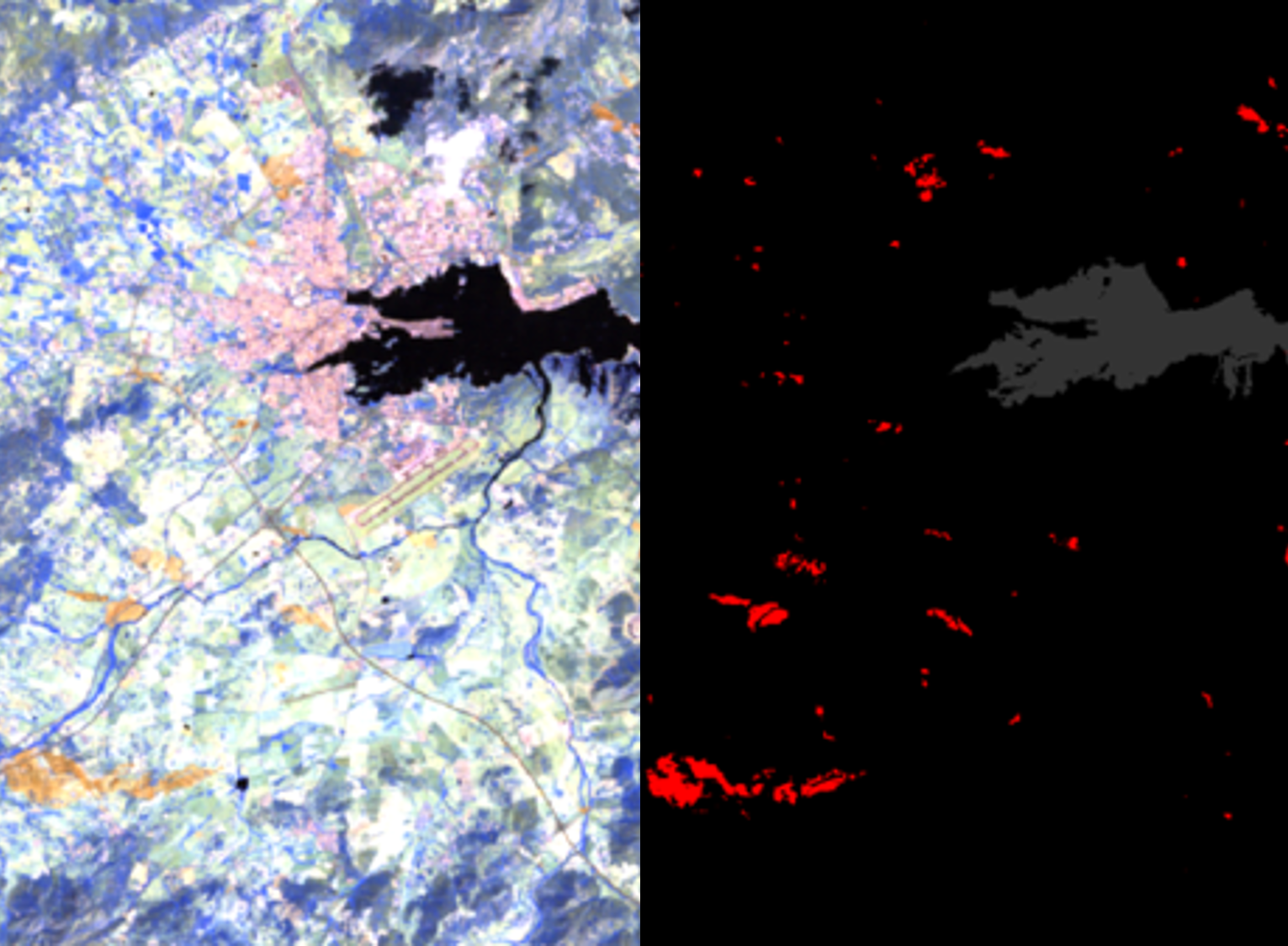
GEO-K processes data from optical sensors in the visible and infrared domain to detect thermal anomalies related to fire hotspots, to identify burnt areas, and to monitor vegetation regeneration. GEO-K processing chain implements also data fusion with radar data to improve the accuracy of the results, combining optical information with radar backscatter coefficient on the same area.
Principal applications include:
- Active fire alerts
- Burned area and burn severity mapping
- Biomass regrowth estimation
GEO-K exploits also Copernicus Services that relate to forest fires, such as the Global Wildfire Information System (a part of the Copernicus Emergency Management Service) and the emissions from wildfires produced within the Global Fire Assimilation System.
GEO-K can provide forest managers and National Agencies with a rapid and accurate assessment of fires.